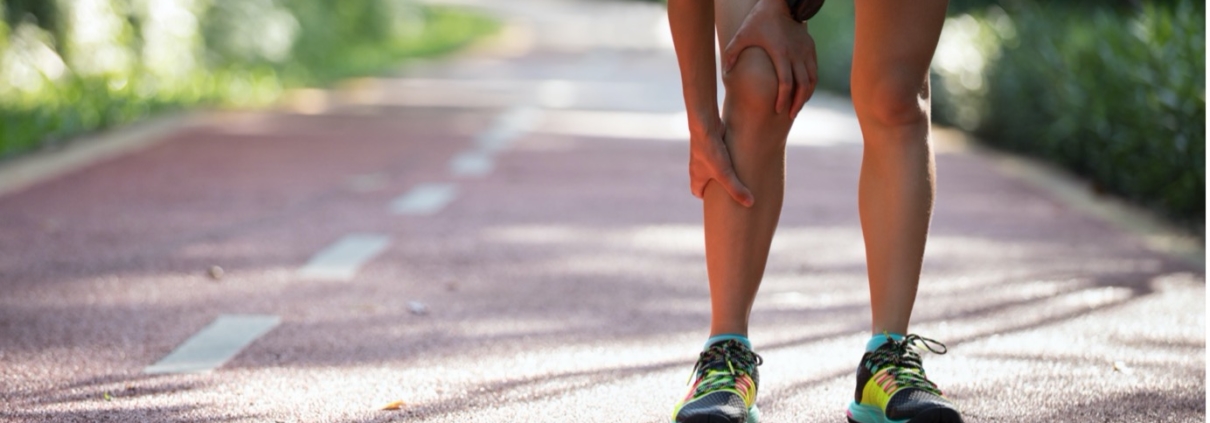
Suffering from shin splints? Don’t run away from the problem!
Along with runner’s knee and Achilles tendinitis – shin splints are thought to be one of the most common health injuries runners incur. And, with a world record-breaking 840,318 people having applied to run the London Marathon on Sunday April 27th, it’s a topic that’s worth talking about.
Shin splints – which are often more formally referred to as medial tibial stress syndrome – are a very common overuse injury. The term refers to a pain that occurs in the front or inner parts of your lower legs, along your shinbone.
According to the latest data, shin splints account for around 11% of injuries in male runners and 17% of injuries in female runners. It’s also prevalent in dancers and those who work in the military.
In total, shin splints affect between 13.6% and 20% of runners and contribute to up to 60% of lower limb injuries
What are the symptoms?
If you suffer from shin splints, you’ll most likely have a dull pain, ache or throbbing feeling along the front or inner part of your shinbone. But you might notice a few other symptoms including:
- A pain that gets worse when you exercise
- Tenderness to touch
- In some cases, mild swelling can occur
- The pain seems to go away when you rest
What is the cause of shin splints?
Shin splints are caused by repetitive stress on your shinbone and the tissues that attach your muscles to the bone.
They occur because you are putting too much stress and strain on your shin bone and the tissues around it.
Why do shin splints occur?
Usually, shin splints flare up because you have overexerted yourself or have pushed your usual exercise limits that little bit further. Generally speaking, you are more likely to get shin splints if you:
- Have started exercising after not being active for some time
- Run or jump on hard surfaces
- Have a poor running technique
- Are wearing shoes that don’t offer you enough cushioning and support
- Don’t rest enough between your exercise sessions
How do you get rid of shin splints or prevent them?
In many cases, shin splints can go away with rest. According to the NHS, if you suffer from shin splints you could also try:
- Wearing trainers that cushion and support your feet properly
- Building up to the exercise intensity gradually
- Warming up before any exercise and stretch after exercising
- Putting an ice pack on your shin for up to 20 minutes every 2 to 3 hours
- Switching to gentle exercise such as yoga or swimming whilst it is healing
- Exercising on soft ground, if and when you are feeling better
How osteopathy can help with shin splints
Osteopathic treatment can help to reduce the tension deep in the muscle of the leg.
With more than 30 years’ experience in the industry, I take a holistic approach when it comes to assessing any problem my clients are suffering from. For shin splints, I would look to reduce the tension in the leg muscles and make sure there are no other underlying mechanical problems.
You might be suffering from the pain in the shin, but other predisposing factors – like your gait or posture – might be the root cause. Only after a full biomechanical assessment can we come up with a treatment plan. If left unchecked these pains might develop into something far more serious.
Robin Kiashek has dealt with numerous running injuries – including shin splints. Get in touch if you would like to book a treatment or find out more.